Assessing thermal loss of buildings
 Did you ever wonder how much of your heating bill is caused by badly insulated windows or walls? Or how much energy you could save by adjusting the temperature level in a room?
Did you ever wonder how much of your heating bill is caused by badly insulated windows or walls? Or how much energy you could save by adjusting the temperature level in a room?
The gSKIN® is the ideal tool for thermal measurements in building physics to answer these questions. The gSKIN® Heat Flux Sensor features:
- Easy read-out
- Simple mounting & integration
- Robustness
How to measure the U-Value of a building and how to analyze the results
Application Note for Building Physics
Applications in building physics
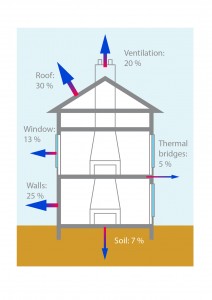
Thermal energy into the building is coming mainly from the heating system and from solar irradiation. The energy exchange between the building and the outside is focused through the roof, walls, windows and thermal bridges e.g. balconies, into the soil and through exchange of ambient air. Thus, a building is a complex thermal system and to optimize it (for example to reduce heating costs) precise data is required.
Use the gSKIN® Heat Flux Sensor to:
- compare the amount of heat transferred through different walls.
- calculate the thermal conductivity (U-value) of walls or windows and find out if you have a well-insulated building.
- quantify the energy balance of a room: How much energy is coming from the heating and where is the energy lost?
- calculate the energy emitted from the heating radiator for example to calculate your heating costs.
- optimize your heating and cooling control.
- analyze the thermal behavior of rooms / buildings at different temperature levels.
Learn more about the technical specifications of the gSKIN® Heat Flux Sensor.
